Consumer Products Goods Industry
Industry Introduction / Features
The consumer products goods industry covers an extremely wide range of products directly consumed by individuals, involving sectors such as food and beverages, personal care, household goods, and apparel. Its products are diverse, ranging from daily necessities like toothpaste and soap to high-end consumer electronics and fashionable clothing. This industry has the following remarkable characteristics. Firstly, consumer demand is highly volatile and extremely sensitive to trends. For example, fashion trends change rapidly, and consumers' preferences for food flavors also evolve continuously. Enterprises must quickly adapt to these changes; otherwise, their products may be phased out in the market. Secondly, brand influence is significant. Well-known brands usually enjoy higher customer loyalty and can set premium prices. A strong brand image can attract consumers and differentiate products from competitors. Thirdly, mass production is common. To meet the large-scale market demand, consumer products companies usually adopt mass production methods to achieve economies of scale, which helps reduce unit production costs. Fourthly, the supply chain is complex. It involves multiple links, including raw material procurement, manufacturing, distribution, and retail. The coordination among different links is crucial for ensuring product availability and timeliness.
General Requirements
In production, consumer products companies face the challenge of balancing production speed and product quality. Due to intense market competition, companies need to quickly launch new products to capture market share. However, the traditional production model relies on manual management, and production lines and equipment form isolated data silos. As a result, the production site is like a black box, making it difficult to obtain real-time production data and unable to provide effective data support for process optimization and efficiency improvement. The production process often depends on experienced operators who rely on their skills and judgment to ensure production capacity and product quality. The application of automation and digitalization technologies can solve these problems. Automated production lines can increase production speed and precision, while digital simulation technologies can optimize the production process in advance, reducing errors and waste. In terms of quality control, although consumer products are not as life-critical as pharmaceuticals, maintaining high quality is still essential for brand reputation. Currently, quality control mainly relies on sampling inspections, which may miss some quality defects. Automation and digitalization can enable real-time monitoring of the production process. For example, in the food industry, sensors can be used to monitor parameters such as temperature and humidity during production and storage, ensuring product safety and quality. In terms of regulatory compliance, consumer products companies need to comply with various regulations, including product safety standards, environmental protection requirements, and labeling regulations. For example, food products must meet strict safety and ingredient labeling requirements. Automation and digital systems can help companies accurately manage and record production data, ensure compliance with regulations, and provide reliable information for product traceability.
Digital Factory Solutions
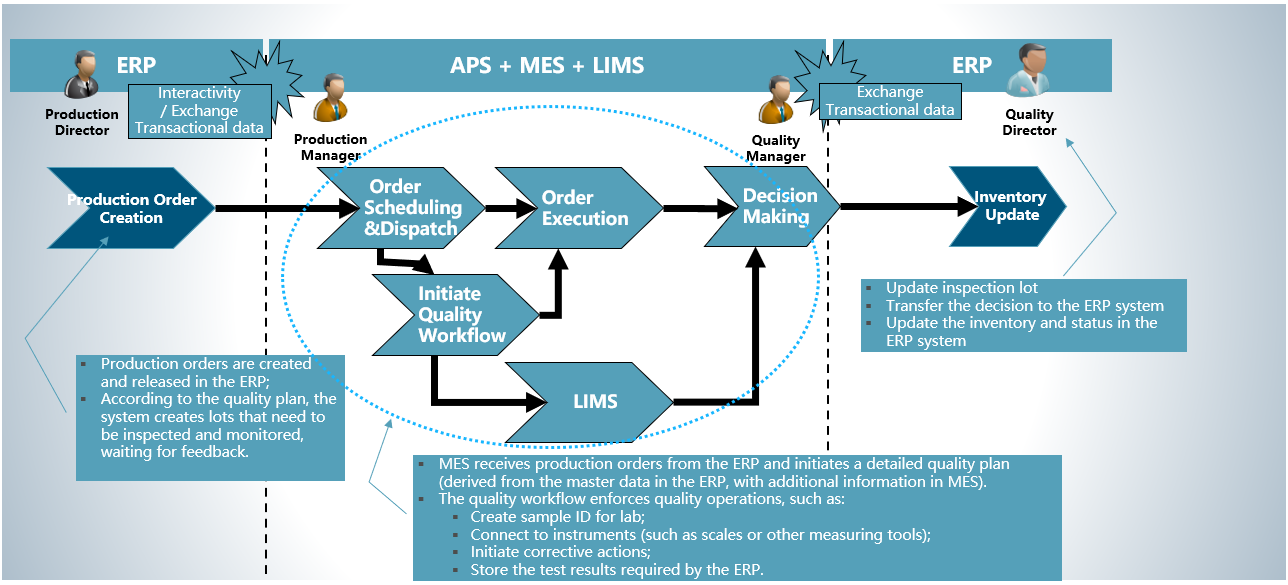
In the increasingly competitive consumer goods industry, enterprises are facing numerous challenges, such as high-quality requirements, cost pressures, compliance challenges, and a rapid increase in product categories and formulations. To help enterprises overcome these difficulties, a comprehensive and efficient Digital Factory Solution for the consumer goods industry has been developed. It consists of APS (Advanced Planning and Scheduling), MES (Manufacturing Execution System), and LIMS (Laboratory Management System). Through their close collaboration, a closed-loop management of plan execution, production quality, and process reporting is formed, creating an integrated intelligent production and operation model for enterprises.
The APS system, based on advanced algorithms, intelligently synchronizes and optimizes the scheduling of ERP orders and work orders. It can not only fully consider detailed production requirements, such as equipment capacity and material supply, and provide accurate production sequences and work item lists, but also predict the impacts of factors like production changes, disruptions, machine failures, and waste. This provides strong support for enterprise decision - making. Enterprises can arrange overtime, prioritize orders, split production batches, and conduct more reasonable delivery date negotiations and order commitments (CTP/ATP) based on this, effectively improving production efficiency and optimizing resource allocation.
The MES system focuses on the integration and synchronization of production processes to achieve precise manufacturing process control. It covers aspects such as formula management, work order management, production management (including production execution and operation instructions), weighing and feeding, material management, equipment management, energy management, and report management. It supports paperless manufacturing and anomaly review, effectively manages automated systems and manual operations, and can be seamlessly integrated with production equipment and automated control systems to achieve the coordination and centralized control of production and online quality, ensuring the high-efficiency, stability of the production process, and the consistency of product quality.
As the core of quality management, the LIMS system is responsible for managing the quality data and workflows in the laboratory. It optimizes the processes of data collection (through instrument devices), inspection, and reporting (including quality deviations), supports the flexible definition and execution of complex test plans and inspection methods, and strictly adheres to quality standards such as GLP and ISO. It is fully integrated with ERP, MES, etc. This not only improves laboratory efficiency and supports the multi - factory model but also saves time and costs, reduces management load, decreases errors, waste rates, and rework situations, provides more accurate decision - making basis for enterprises, and strengthens the group's QA/QC process.
Through the close cooperation of APS, MES, and LIMS systems, enterprises have achieved a closed - loop management from plan formulation to production execution, quality control, and process reporting. Real - time data during the production process flows seamlessly among various systems, realizing production transparency and improving the real - time nature of process control. Enterprises can promptly identify and solve problems, continuously optimize the production process, and enhance product quality and compliance control levels. At the same time, this integrated solution shortens the new product launch cycle, improves the enterprise's business collaboration ability, production flexibility, and data consistency, effectively reduces the complexity of the production process, enhances product quality assurance capabilities, and precise product recall capabilities, comprehensively helping consumer goods enterprises enhance their value and core competitiveness and stand out in the market competition in the digital age.